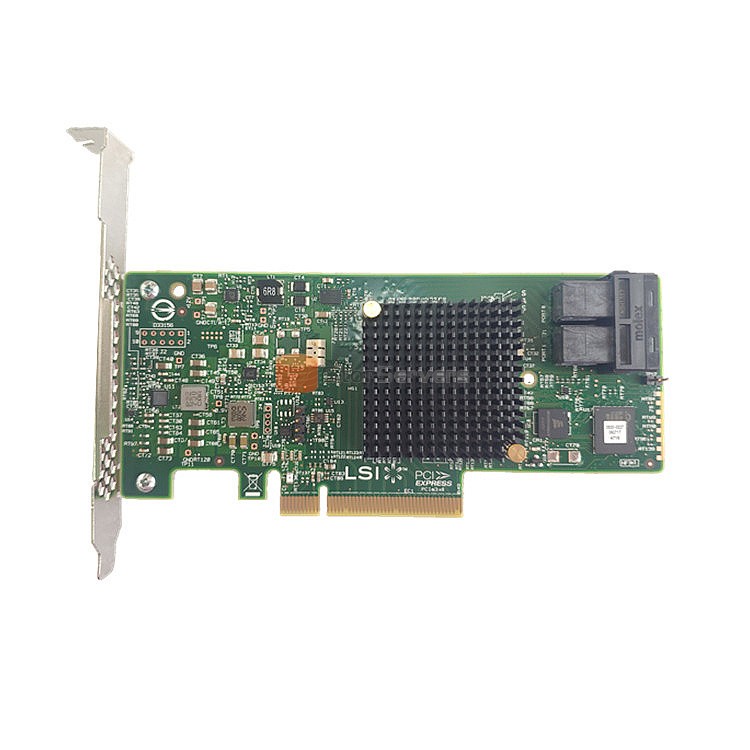
 Structure of a RAID card
Sep 14, 2023
Structure of a RAID card
Sep 14, 2023
Today let's continue to talk about the structure of the raid card.
RAID card with CPU seems to be a small computer system, has its own CPU, memory, ROM, bus and IO interface, but this small computer is to serve the big computer.
It is important to include the SCSI controller on the SCSI RAID card, because the physical SCSI disks are still attached to the back end. Its front end is connected to the PCI bus of the host, so there must be a PCI bus controller to maintain the PCI bus arbitration, data sending and receiving functions. Also need to have a ROM, is generally used as a Flash chip ROM, which stores the initialization of the RAID card necessary code and the implementation of the RAID function required code.
The role of RAM, first of all, is as a data cache to improve performance; Secondly, it is the memory space required by the CPU on the RAID card to perform RAID operations. XOR chip is specially used to do parity data calculation of RAID3, 5, 6 and so on. Letting the CPU do the validation would require code execution, which would take many cycles. However, if a dedicated digital circuit is used directly, the result is obtained immediately as soon as it is in and out. Therefore, in order to get rid of the CPU, the circuit module specially used for XOR operation is added, which greatly increases the speed of data check calculation.
The difference between RAID card and SCSI card is the RAID function, the other is not too different. A RAID card is called a multi-channel RAID card if there are multiple SCSI channels on it. At present, the SCSI RAID card has up to 4 channels, and its back end can be connected to 4 SCSI buses, so up to 64 SCSI devices (16 bit bus) can be connected.
With the addition of RAID functionality, the SCSI controller becomes a puppet of the RAID program code and does whatever the RAID tells it to do. The SCSI controller is fully aware of the disks under its control and communicates with the RAID application code. Once the RAID code knows which disks are in the SCSI controller's hands, it can adjust the RAID code to use ROM options such as RAID type, strip size, and so on, instructing its dummy SCSI controller to report "virtual" logical disks to the host instead of all physical disks.
Hint: RAID has a concept of striping in mind. By striping, we don't really mean dividing the disk into bars and strips as in low-level formatting. This striping is all "in the mind," that is, in the program code. Because once the position and size of the strip are set, they are fixed. An LBA address block on a virtual disk corresponds to one or more LBA blocks on the real disk, and these mappings are predefined through the configuration interface. And a certain RAID algorithm is often embodied in some complex formulas, rather than using a table to record the corresponding LBA of each virtual disk and physical disk, so the efficiency will be poor. After each 10 arrives, RAID has to query this table to obtain the LBA of the corresponding physical disk, and the query speed is very slow, let alone in the face of such a large table. If we use a functional relationship formula between logical LBA and physical LBA to do the operation, the speed is very fast.
Because mapping is performed entirely by formula, no flags are ever written to the physical disk to mark the so-called strips. The concept of a strip is only logical and does not exist physically. Therefore, the concept of strip only "memory" in the RAID program code can be, to change is to change the program code can be. The only thing that needs to be written to the disk is some RAID information, so that even if the disk is removed and placed on another RAID card of the same model, the previously made RAID information can be correctly recognized. The SNIA association has defined a standard format of DDFRAID information, requiring all RAID card manufacturers to store RAID information in accordance with this standard, so that all RAID cards are common.
After striding, the RAID application code directs the SCSI controller to submit a virtualized "virtual disk" or "logical disk," or simply a LUN, to the OS-level driver code. 1. Structure of a RAID card
RAID card with CPU seems to be a small computer system, has its own CPU, memory, ROM, bus and IO interface, but this small computer is to serve the big computer.
It is important to include the SCSI controller on the SCSI RAID card, because the physical SCSI disks are still attached to the back end. Its front end is connected to the PCI bus of the host, so there must be a PCI bus controller to maintain the PCI bus arbitration, data sending and receiving functions. Also need to have a ROM, is generally used as a Flash chip ROM, which stores the initialization of the RAID card necessary code and the implementation of the RAID function required code.
The role of RAM, first of all, is as a data cache to improve performance; Secondly, it is the memory space required by the CPU on the RAID card to perform RAID operations. XOR chip is specially used to do parity data calculation of RAID3, 5, 6 and so on. Letting the CPU do the validation would require code execution, which would take many cycles. However, if a dedicated digital circuit is used directly, the result is obtained immediately as soon as it is in and out. Therefore, in order to get rid of the CPU, the circuit module specially used for XOR operation is added, which greatly increases the speed of data check calculation.
The difference between RAID card and SCSI card is the RAID function, the other is not too different. A RAID card is called a multi-channel RAID card if there are multiple SCSI channels on it. At present, the SCSI RAID card has up to 4 channels, and its back end can be connected to 4 SCSI buses, so up to 64 SCSI devices (16 bit bus) can be connected.
With the addition of RAID functionality, the SCSI controller becomes a puppet of the RAID program code and does whatever the RAID tells it to do. The SCSI controller is fully aware of the disks under its control and communicates with the RAID application code. Once the RAID code knows which disks are in the SCSI controller's hands, it can adjust the RAID code to use ROM options such as RAID type, strip size, and so on, instructing its dummy SCSI controller to report "virtual" logical disks to the host instead of all physical disks.
Hint: RAID has a concept of striping in mind. By striping, we don't really mean dividing the disk into bars and strips as in low-level formatting. This striping is all "in the mind," that is, in the program code. Because once the position and size of the strip are set, they are fixed. An LBA address block on a virtual disk corresponds to one or more LBA blocks on the real disk, and these mappings are predefined through the configuration interface. And a certain RAID algorithm is often embodied in some complex formulas, rather than using a table to record the corresponding LBA of each virtual disk and physical disk, so the efficiency will be poor. After each 10 arrives, RAID has to query this table to obtain the LBA of the corresponding physical disk, and the query speed is very slow, let alone in the face of such a large table. If we use a functional relationship formula between logical LBA and physical LBA to do the operation, the speed is very fast.
Because mapping is performed entirely by formula, no flags are ever written to the physical disk to mark the so-called strips. The concept of a strip is only logical and does not exist physically. Therefore, the concept of strip only "memory" in the RAID program code can be, to change is to change the program code can be. The only thing that needs to be written to the disk is some RAID information, so that even if the disk is removed and placed on another RAID card of the same model, the previously made RAID information can be correctly recognized. The SNIA association has defined a standard format of DDFRAID information, requiring all RAID card manufacturers to store RAID information in accordance with this standard, so that all RAID cards are common.
After striding, the RAID application code directs the SCSI controller to submit a virtualized "virtual disk" or "logical disk," or simply a LUN, to the OS-level driver code.
We through several articles detailed introduction of raid card, I believe you have a deeper understanding of raid card. If you have a lot of questions about server accessories, storage, then welcome to consult, it is my pleasure to answer your questions. STOR Technology Limited will also provide you with a large number of original high-performance products, such as: lsi 9480 8i8e, lsi 9361 4i, lsi 9341 8i and so on, three-year warranty and unsurpassed factory price to reduce your concerns.
 Two Write Modes of RAID Card Cache
Sep 02, 2024
Two Write Modes of RAID Card Cache
Sep 02, 2024
 Use computers to process information and save data
Mar 21, 2024
Use computers to process information and save data
Mar 21, 2024
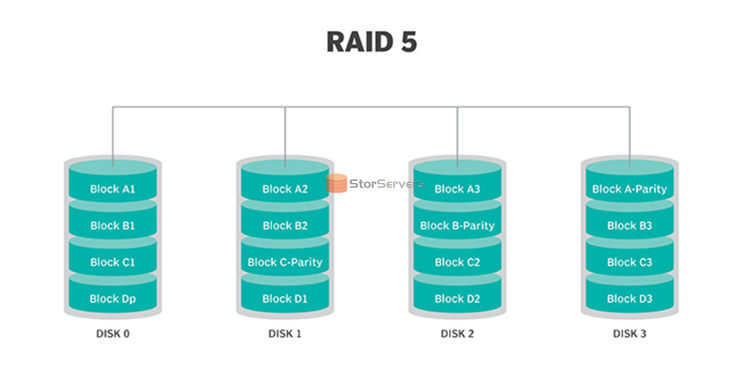 What is RAID 5?
Feb 24, 2024
What is RAID 5?
Feb 24, 2024
 Get information on the model number of the network card
Jan 04, 2024
Get information on the model number of the network card
Jan 04, 2024
 Application of MCX4421A-ACQN high performance network adapter
Dec 16, 2023
Application of MCX4421A-ACQN high performance network adapter
Dec 16, 2023
 MegaRAID 9580-8i8e Key Features
Dec 06, 2023
MegaRAID 9580-8i8e Key Features
Dec 06, 2023
 Port type of the RAID card
Nov 08, 2023
Port type of the RAID card
Nov 08, 2023
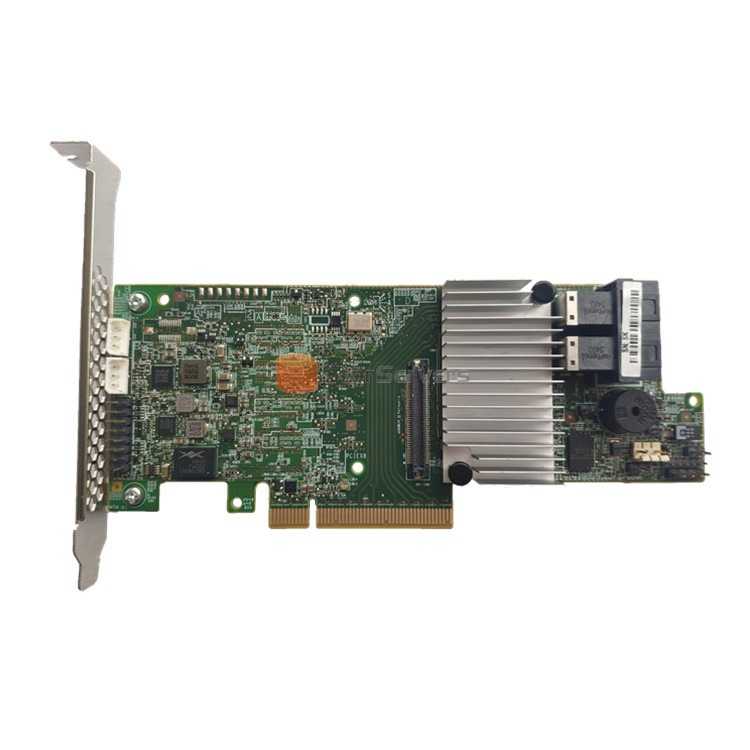 The initialization process after the RAID is configured
Oct 12, 2023
The initialization process after the RAID is configured
Oct 12, 2023
 Structure of a RAID card
Sep 14, 2023
Structure of a RAID card
Sep 14, 2023
 What are the drawbacks of software raid? How to implement raid in hardware?
Sep 08, 2023
What are the drawbacks of software raid? How to implement raid in hardware?
Sep 08, 2023
 Implementation and configuration of RAID in operating system
Sep 07, 2023
Implementation and configuration of RAID in operating system
Sep 07, 2023
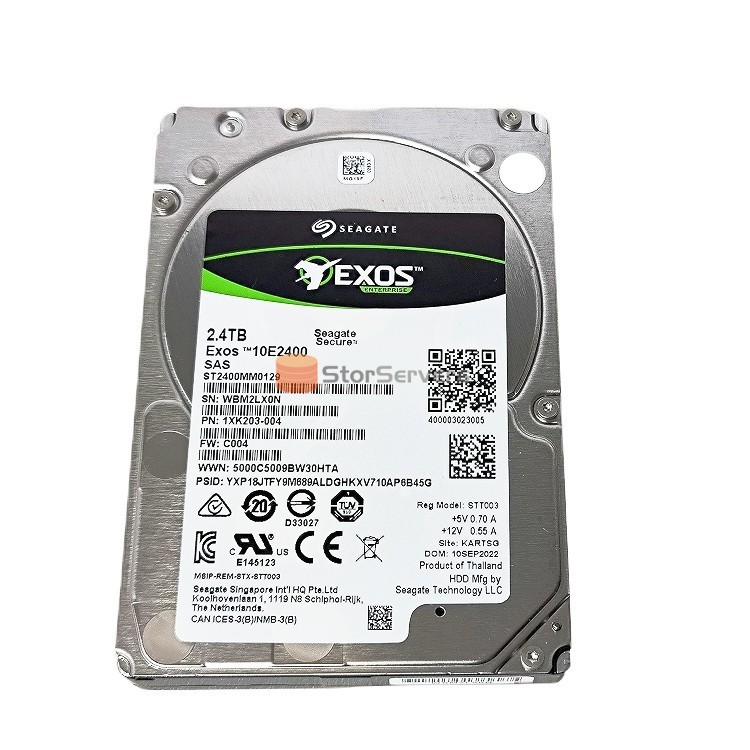 Seagate ST2400MM0129 SAS hard drive HDD for servers
Jul 06, 2023
Seagate ST2400MM0129 SAS hard drive HDD for servers
Jul 06, 2023